X-linked Recessive (2) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 X-linked recessive inheritance is a mode of
X-linked recessive inheritance is a mode of
 In humans, inheritance of X-linked recessive traits follows a unique pattern made up of three points.
* The first is that affected fathers cannot pass X-linked recessive traits to their sons because fathers give Y chromosomes to their sons. This means that males affected by an X-linked recessive disorder inherited the responsible X chromosome from their mothers.
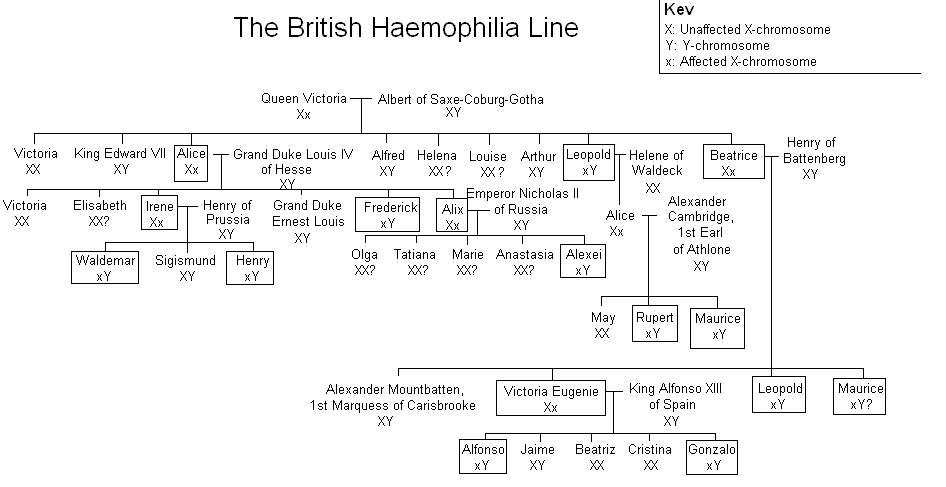
* Second, X-linked recessive traits are more commonly expressed in males than females. This is due to the fact that males possess only a single X chromosome, and therefore require only one mutated X in order to be affected. Women possess two X chromosomes, and thus must receive two of the mutated recessive X chromosomes (one from each parent). A popular example showing this pattern of inheritance is that of the descendants of Queen Victoria and the blood disease
In humans, inheritance of X-linked recessive traits follows a unique pattern made up of three points.
* The first is that affected fathers cannot pass X-linked recessive traits to their sons because fathers give Y chromosomes to their sons. This means that males affected by an X-linked recessive disorder inherited the responsible X chromosome from their mothers.
* Second, X-linked recessive traits are more commonly expressed in males than females. This is due to the fact that males possess only a single X chromosome, and therefore require only one mutated X in order to be affected. Women possess two X chromosomes, and thus must receive two of the mutated recessive X chromosomes (one from each parent). A popular example showing this pattern of inheritance is that of the descendants of Queen Victoria and the blood disease
Retrieved on 5 Mars, 2009 * Red–green color blindness, a very common trait in humans and frequently used to explain X-linked disorders. Between seven and ten percent of men and 0.49% to 1% of women are affected. Its commonness may be explained by its relatively benign nature. It is also known as daltonism. *
X-linked diseases
from the
Sex-linked recessive: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
Genetics
inheritance
Inheritance is the practice of receiving private property, Title (property), titles, debts, entitlements, Privilege (law), privileges, rights, and Law of obligations, obligations upon the death of an individual. The rules of inheritance differ ...
in which a mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mi ...
in a gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
on the X chromosome
The X chromosome is one of the two sex-determining chromosomes (allosomes) in many organisms, including mammals (the other is the Y chromosome), and is found in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and XO sex-d ...
causes the phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological proper ...
to be always expressed in males (who are necessarily homozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mo ...
for the gene mutation because they have one X and one Y chromosome
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in therian mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is normally the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or abse ...
) and in females who are homozygous for the gene mutation, see zygosity
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mo ...
. Females with one copy of the mutated gene are carriers.
X-linked inheritance means that the gene causing the trait or the disorder is located on the X chromosome. Females have two X chromosomes while males have one X and one Y chromosome
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in therian mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is normally the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or abse ...
. Carrier females who have only one copy of the mutation do not usually express the phenotype, although differences in X-chromosome inactivation
X-inactivation (also called Lyonization, after English geneticist Mary Lyon) is a process by which one of the copies of the X chromosome is inactivated in therian female mammals. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by being packaged into ...
(known as skewed X-inactivation
Skewed X-chromosome inactivation (skewed X-inactivation) occurs when the X-inactivation of one X chromosome is favored over the other, leading to an uneven number of cells with each chromosome inactivated. It is usually defined as one allele being ...
) can lead to varying degrees of clinical expression in carrier females, since some cells will express one X allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ἄλλος ''állos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
and some will express the other. The current estimate of sequenced X-linked genes is 499, and the total, including vaguely defined traits, is 983.
Patterns of inheritance
hemophilia
Haemophilia, or hemophilia (), is a mostly inherited genetic disorder that impairs the body's ability to make blood clots, a process needed to stop bleeding. This results in people bleeding for a longer time after an injury, easy bruising, ...
.
* The last pattern seen is that X-linked recessive traits tend to skip generations, meaning that an affected grandfather will not have an affected son, but could have an affected grandson through his daughter. Explained further, all daughters of an affected man will obtain his mutated X, and will then be either carriers or affected themselves depending on the mother. The resulting sons will either have a 50% chance of being affected (mother is carrier), or 100% chance (mother is affected). It is because of these percentages that we see males more commonly affected than females.
Pushback on recessive/dominant terminology
A few scholars have suggested discontinuing the use of the terms ''dominant'' and ''recessive'' when referring to X-linked inheritance. The possession of two X chromosomes in females leads to dosage issues which are alleviated byX-inactivation
X-inactivation (also called Lyonization, after English geneticist Mary Lyon) is a process by which one of the copies of the X chromosome is inactivated in therian female mammals. The inactive X chromosome is silenced by being packaged into ...
. Stating that the highly variable penetrance
Penetrance in genetics is the proportion of individuals carrying a particular variant (or allele) of a gene (the genotype) that also express an associated trait (the phenotype). In medical genetics, the penetrance of a disease-causing mutation is t ...
of X-linked traits in females as a result of mechanisms such as skewed X-inactivation or somatic mosaicism
Mosaicism or genetic mosaicism is a condition in multicellular organisms in which a single organism possesses more than one genetic line as the result of genetic mutation. This means that various genetic lines resulted from a single fertilized e ...
is difficult to reconcile with standard definitions of dominance and recessiveness, scholars have suggested referring to traits on the X chromosome simply as ''X-linked.''
Examples
Most common
The most common X-linked recessive disorders are:GP Notebook - X-linked recessive disordersRetrieved on 5 Mars, 2009 * Red–green color blindness, a very common trait in humans and frequently used to explain X-linked disorders. Between seven and ten percent of men and 0.49% to 1% of women are affected. Its commonness may be explained by its relatively benign nature. It is also known as daltonism. *
Hemophilia A
Haemophilia A (or hemophilia A) is a genetic deficiency in clotting factor VIII, which causes increased bleeding and usually affects males. In the majority of cases it is inherited as an X-linked recessive trait, though there are cases which arise ...
, a blood clotting
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechanism o ...
disorder caused by a mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mi ...
of the Factor VIII
Factor VIII (FVIII) is an essential blood-clotting protein, also known as anti-hemophilic factor (AHF). In humans, factor VIII is encoded by the ''F8'' gene. Defects in this gene result in hemophilia A, a recessive X-linked coagulation disorder. ...
gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
and leading to a deficiency of Factor VIII. It was once thought to be the "royal disease" found in the descendants of Queen Victoria. This is now known to have been Hemophilia B (see below).
* Hemophilia B
Haemophilia B, also spelled hemophilia B, is a blood clotting disorder causing easy bruising and bleeding due to an inherited mutation of the gene for factor IX, and resulting in a deficiency of factor IX. It is less common than factor VIII defi ...
, also known as Christmas disease, a blood clotting
Coagulation, also known as clotting, is the process by which blood changes from a liquid to a gel, forming a blood clot. It potentially results in hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, followed by repair. The mechanism o ...
disorder caused by a mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mi ...
of the Factor IX
Factor IX (or Christmas factor) () is one of the serine proteases of the coagulation system; it belongs to peptidase family S1. Deficiency of this protein causes haemophilia B. It was discovered in 1952 after a young boy named Stephen Christmas w ...
gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba ...
and leading to a deficiency of Factor IX. It is rarer than hemophilia A
Haemophilia A (or hemophilia A) is a genetic deficiency in clotting factor VIII, which causes increased bleeding and usually affects males. In the majority of cases it is inherited as an X-linked recessive trait, though there are cases which arise ...
. As noted above, it was common
Common may refer to:
Places
* Common, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland
* Boston Common, a central public park in Boston, Massachusetts
* Cambridge Common, common land area in Cambridge, Massachusetts
* Clapham Common, originally com ...
among the descendants of Queen Victoria.
* Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a severe type of muscular dystrophy that primarily affects boys. Muscle weakness usually begins around the age of four, and worsens quickly. Muscle loss typically occurs first in the thighs and pelvis fol ...
, which is associated with mutations in the dystrophin
Dystrophin is a rod-shaped cytoplasmic protein, and a vital part of a protein complex that connects the cytoskeleton of a muscle fiber to the surrounding extracellular matrix through the cell membrane. This complex is variously known as the costa ...
gene. It is characterized by rapid progression of muscle degeneration, eventually leading to loss of skeletal muscle control, respiratory failure, and death.
* Becker's muscular dystrophy
Becker muscular dystrophy is an X-linked recessive inherited disorder characterized by slowly progressing muscle weakness of the legs and pelvis. It is a type of dystrophinopathy. This is caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene, which encodes ...
, a milder form of Duchenne, which causes slowly progressive muscle weakness of the legs and pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The ...
.
* X-linked ichthyosis X-linked ichthyosis (abbreviated ''XLI'') is a skin condition caused by the genetic disorder, hereditary deficiency of the steroid sulfatase (STS) enzyme that affects 1 in 2000 to 1 in 6000 males.
XLI manifests with dry, scaly skin and is due to d ...
, a form of ichthyosis
Ichthyosis is a family of genetic skin disorders characterized by dry, thickened, scaly skin. The more than 20 types of ichthyosis range in severity of symptoms, outward appearance, underlying genetic cause and mode of inheritance (e.g., dominan ...
caused by a hereditary deficiency of the steroid sulfatase
Steroid sulfatase (STS), or steryl-sulfatase (EC 3.1.6.2), formerly known as arylsulfatase C, is a sulfatase enzyme involved in the metabolism of steroids. It is encoded by the ''STS'' gene.
Reactions
This enzyme catalysis, catalyses the follow ...
(STS) enzyme. It is fairly rare, affecting one in 2,000 to one in 6,000 males.
* X-linked agammaglobulinemia
X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA) is a rare genetic disorder discovered in 1952 that affects the body's ability to fight infection. As the form of agammaglobulinemia that is X-linked, it is much more common in males. In people with XLA, the lymphop ...
(XLA), which affects the body's ability to fight infection. XLA patients do not generate mature B cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or ...
s. B cells are part of the immune system and normally manufacture antibodies (also called immunoglobulin
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
s) which defends the body from infections (the humoral
Humoral immunity is the aspect of immunity that is mediated by macromolecules - including secreted antibodies, complement proteins, and certain antimicrobial peptides - located in extracellular fluids. Humoral immunity is named so because it invo ...
response). Patients with untreated XLA are prone to develop serious and even fatal infections.
* Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PDD), which is the most common enzyme deficiency worldwide, is an inborn error of metabolism that predisposes to red blood cell breakdown. Most of the time, those who are affected have no symptoms. ...
, which causes nonimmune hemolytic anemia in response to a number of causes, most commonly infection or exposure to certain medications, chemicals, or foods. Commonly known as "favism", as it can be triggered by chemicals existing naturally in broad (or fava) beans.
Less common disorders
Theoretically, a mutation in any of the genes on chromosome X may cause disease, but below are some notable ones, with short description of symptoms: *Adrenoleukodystrophy
Adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) is a disease linked to the X chromosome. It is a result of fatty acid buildup caused by peroxisomal fatty acid beta oxidation which results in the accumulation of very long chain fatty acids in tissues throughout the bo ...
; leads to progressive brain damage, failure of the adrenal glands and eventually death.
* Alport syndrome
Alport syndrome is a genetic disorder affecting around 1 in 5,000-10,000 children, characterized by glomerulonephritis, end-stage kidney disease, and hearing loss. Alport syndrome can also affect the eyes, though the changes do not usually affect v ...
; glomerulonephritis, endstage kidney disease, and hearing loss. A minority of Alport syndrome cases are due to an autosomal recessive mutation in the gene coding for type IV collagen
Collagen IV (ColIV or Col4) is a type of collagen found primarily in the basal lamina. The collagen IV C4 domain at the C-terminus is not removed in post-translational processing, and the fibers link head-to-head, rather than in parallel. Also, ...
.
* Androgen insensitivity syndrome
Androgen insensitivity syndrome (AIS) is a difference in sex development involving hormonal resistance due to androgen receptor dysfunction.
It affects 1 in 20,000 to 64,000 XY ( karyotypically male) births. The condition results in the partial o ...
; variable degrees of undervirilization and/or infertility in XY persons of either sex
* Barth syndrome
Barth syndrome (BTHS) is a rare but serious X-linked genetic disorder, caused by changes in phospholipid structure and metabolism. It may affect multiple body systems (though mainly characterized by pronounced pediatric-onset cardiomyopathy), and ...
; metabolism distortion, delayed motor skills, stamina deficiency, hypotonia, chronic fatigue, delayed growth, cardiomyopathy, and compromised immune system.
* Blue cone monochromacy
Blue-cone monochromacy (BCM) is an inherited eye disease that causes severe color blindness, poor visual acuity, nystagmus and photophobia due to the absence of functional red (L) and green (M) cone photoreceptor cells in the retina. BCM is a re ...
; low vision acuity, color blindness, photophobia, infantile nystagmus.
* Centronuclear myopathy
Centronuclear myopathies (CNM) are a group of congenital myopathies where cell nuclei are abnormally located in the center of muscle cells instead of their normal location at the periphery.
Symptoms of CNM include severe hypotonia, hypoxia-requi ...
; where cell nuclei are abnormally located in skeletal muscle cells. In CNM the nuclei are located at a position in the center of the cell, instead of their normal location at the periphery.
* Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease (CMTX2-3); disorder of nerves (neuropathy) that is characterized by loss of muscle tissue and touch sensation, predominantly in the feet and legs but also in the hands and arms in the advanced stages of disease.
* Coffin–Lowry syndrome
Coffin–Lowry syndrome is a genetic disorder that is X-linked dominant and which causes severe mental problems sometimes associated with abnormalities of growth, cardiac abnormalities, kyphoscoliosis, as well as auditory and visual abnormalities.
...
; severe intellectual disability sometimes associated with abnormalities of growth, cardiac abnormalities, kyphoscoliosis as well as auditory and visual abnormalities.
* Fabry disease
Fabry disease, also known as Anderson–Fabry disease, is a rare genetic disease that can affect many parts of the body, including the kidneys, heart, and skin. Fabry disease is one of a group of conditions known as lysosomal storage diseases. T ...
; A lysosomal storage disease causing anhidrosis, fatigue, angiokeratomas, burning extremity pain and ocular involvement.
* Hunter syndrome
Hunter syndrome, or mucopolysaccharidosis type II (MPS II), is a rare genetic disorder in which large sugar molecules called glycosaminoglycans (or GAGs or mucopolysaccharides) build up in body tissues. It is a form of lysosomal storage disease. ...
; potentially causing hearing loss, thickening of the heart valves leading to a decline in cardiac function, obstructive airway disease, sleep apnea, and enlargement of the liver and spleen.
* Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia is one of about 150 types of ectodermal dysplasia in humans. Before birth, these disorders result in the abnormal development of structures including the skin, hair, nails, teeth, and sweat glands.Freedberg, et al ...
, presenting with hypohidrosis, hypotrichosis, hypodontia
* Kabuki syndrome
Kabuki syndrome (also previously known as Kabuki-makeup syndrome (KMS) or Niikawa–Kuroki syndrome) is a congenital disorder of genetic origin. It affects multiple parts of the body, with varying symptoms and severity, although the most common is ...
(the ''KDM6A
Lysine-specific demethylase 6A also known as Ubiquitously transcribed tetratricopeptide repeat, X chromosome (UTX), is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''KDM6A'' gene. It belongs to the 2-oxoglutarate (2OG)-dependent dioxygenase super ...
'' variant); multiple congenital anomalies and intellectual disability.
* Spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy
Spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy (SBMA), popularly known as Kennedy's disease, is a debilitating neurodegenerative disorder resulting in muscle cramps and progressive weakness due to degeneration of motor neurons in the brainstem and spinal cor ...
; muscle cramps and progressive weakness
* Lesch–Nyhan syndrome
Lesch–Nyhan syndrome (LNS) is a rare inherited disorder caused by a deficiency of the enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT). This deficiency occurs due to mutations in the ''HPRT1'' gene located on the X chromosome. LNS ...
; neurologic dysfunction, cognitive and behavioral disturbances including self-mutilation, and uric acid overproduction (hyperuricemia)
* Lowe syndrome
Oculocerebrorenal syndrome (also called Lowe syndrome) is a rare X-linked recessive disorder characterized by congenital cataracts, hypotonia, intellectual disability, proximal tubular acidosis, aminoaciduria and low-molecular-weight proteinuria. L ...
; hydrophthalmia, cataracts, intellectual disabilities, aminoaciduria, reduced renal ammonia production and vitamin D-resistant rickets
* Menkes disease
Menkes disease (MNK), also known as Menkes syndrome, is an X-linked recessive disorder caused by mutations in genes coding for the copper-transport protein ATP7A, leading to copper deficiency. Characteristic findings include kinky hair, growth ...
; sparse and coarse hair, growth failure, and deterioration of the nervous system
* Nasodigitoacoustic syndrome; misshaped nose, brachydactyly
Brachydactyly (Greek βραχύς = "short" plus δάκτυλος = "finger"), is a medical term which literally means "short finger". The shortness is relative to the length of other long bones and other parts of the body. Brachydactyly is an in ...
of the distal phalanges
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones.
...
, sensorineural deafness
* Nonsyndromic deafness
Nonsyndromic deafness is hearing loss that is not associated with other signs and symptoms. In contrast, syndromic deafness involves hearing loss that occurs with abnormalities in other parts of the body. Genetic changes are related to the followi ...
; hearing loss
* Norrie disease
Norrie disease is a rare disease and genetic disorder that primarily affects the eyes and almost always leads to blindness. It is caused by mutations in the ''Norrin cystine knot growth factor (NDP)'' gene, which is located on the X chromosome. In ...
; cataracts, leukocoria along with other developmental issues in the eye
* Occipital horn syndrome
Occipital horn syndrome (OHS), formerly considered a variant of Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, is an X-linked recessive mitochondrial and connective tissue disorder. It is caused by a deficiency in the transport of the essential mineral copper, associ ...
; deformations in the skeleton
* Ocular albinism
Ocular albinism is a form of albinism which, in contrast to oculocutaneous albinism, presents primarily in the eyes. There are multiple forms of ocular albinism, which are clinically similar.James, William; Berger, Timothy; Elston, Dirk (2005). ' ...
; lack of pigmentation in the eye
* Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency
Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency also known as OTC deficiency is the most common urea cycle disorder in humans. Ornithine transcarbamylase, the defective enzyme in this disorder is the final enzyme in the proximal portion of the urea cycle, re ...
; developmental delay and intellectual disability. Progressive liver damage, skin lesions, and brittle hair may also be seen
* Oto-palato-digital syndrome
Oto-palato-digital syndrome is the generalised term for two conditions, oto-palato-digital syndrome type I (OPD1) and oto-palato-digital syndrome type II (OPD2), that are both X-linked recessive genetic disorders with overlapping phenotypes. The mo ...
; facial deformities, cleft palate, hearing loss
* Siderius X-linked mental retardation syndrome
PHD finger protein 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PHF8'' gene.
Function
PHF8 belongs to the family of ferrous iron and alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases superfamily., and is active as a histone lysine demethylase wi ...
; cleft lip and palate with intellectual disability and facial dysmorphism, caused by mutations in the histone demethylase PHF8
PHD finger protein 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PHF8'' gene.
Function
PHF8 belongs to the family of ferrous iron and alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases superfamily., and is active as a histone lysine demethylase wi ...
* Simpson–Golabi–Behmel syndrome
Simpson–Golabi–Behmel syndrome (SGBS), is a rare inherited congenital disorder that can cause craniofacial, skeletal, cardiac, and renal abnormalities.
The syndrome is inherited in an X-linked recessive fashion, where males express the phenoty ...
; coarse faces with protruding jaw and tongue, widened nasal bridge, and upturned nasal tip
* Spinal muscular atrophy
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a rare neuromuscular disorder that results in the loss of motor neurons and progressive muscle wasting. It is usually diagnosed in infancy or early childhood and if left untreated it is the most common genetic ...
caused by UBE1 gene mutation; weakness due to loss of the motor neurons of the spinal cord and brainstem
* Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome
Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome (WAS) is a rare X-linked recessive disease characterized by eczema, thrombocytopenia (low platelet count), immune deficiency, and bloody diarrhea (secondary to the thrombocytopenia). It is also sometimes called the eczem ...
; eczema, thrombocytopenia, immune deficiency, and bloody diarrhea
* X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency (X-SCID) is an immunodeficiency disorder in which the body produces very few T cells and NK cells.
In the absence of T cell help, B cells become defective. It is an X-linked recessive inheritance trait, ...
(SCID); infections, usually causing death in the first years of life
* X-linked sideroblastic anemia; skin paleness, fatigue, dizziness and enlarged spleen and liver.
See also
*Sex linkage
Sex linked describes the sex-specific patterns of inheritance and presentation when a gene mutation (allele) is present on a sex chromosome (allosome) rather than a non-sex chromosome (autosome). In humans, these are termed X-linked recessive, ...
* X-linked dominant inheritance
X-linked dominant inheritance, sometimes referred to as X-linked dominance, is a mode of genetic inheritance by which a dominant gene is carried on the X chromosome. As an inheritance pattern, it is less common than the X-linked recessive type. ...
References
External links
X-linked diseases
from the
Wellcome Trust
The Wellcome Trust is a charitable foundation focused on health research based in London, in the United Kingdom. It was established in 1936 with legacies from the pharmaceutical magnate Henry Wellcome (founder of one of the predecessors of Glaxo ...
{{X-linked disorders
emale X-linked disordersSex-linked recessive: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia
Genetics